The urinary system plays a far more sophisticated role than simply eliminating fluid from the body. At its core, it is a vital regulator of metabolic waste, particularly nitrogen-rich compounds produced during protein metabolism. The kidneys — key organs within this system — act as filtration centers, endocrine glands, and homeostasis managers. They help convert toxic ammonia into soluble urea, fine-tune electrolyte concentrations, manage blood pressure through hormonal release, and enable critical processes like red blood cell production and calcium absorption. This longform explainer outlines how the urinary system functions, why kidney health is central to modern physiology, and how this intricate network impacts both everyday wellness and medical intervention.
Why does the human body create nitrogenous waste?
Nitrogenous waste arises primarily from the breakdown of amino acids during protein metabolism. As cells utilize proteins for energy production, repair, and synthesis, they generate ammonia — a highly toxic substance. Ammonia cannot linger in the bloodstream, as even minor accumulations can disrupt neural function and cellular integrity. To mitigate this, the liver converts ammonia into urea through the urea cycle. Urea is water-soluble, far less toxic, and can be efficiently transported through the bloodstream to the kidneys. Unlike carbon dioxide or water vapor, which can be exhaled through the lungs, nitrogenous waste cannot be transformed into a gas and expelled in breath. The body depends on its urinary system to manage this load through a tightly regulated filtration and excretion mechanism.
How does the urinary system eliminate urea from the bloodstream?
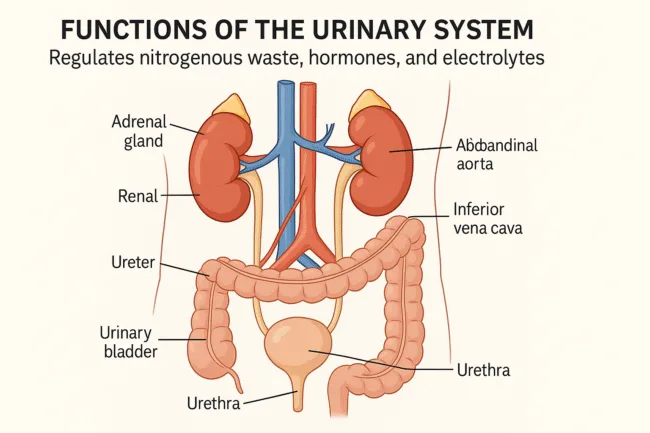
The urinary system comprises several interconnected structures that collectively filter blood, create urine, and expel it from the body. These structures include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Each kidney contains approximately one million microscopic filtering units called nephrons. Blood enters the kidneys through the renal artery and undergoes initial filtration in the glomerulus, a capillary network that separates small molecules from blood cells and proteins. Urea, water, salts, and acids pass through into the renal tubules, where further processing determines what will be reabsorbed into the bloodstream and what will be eliminated.
Urine formation is the result of this process. Once formed, urine flows through the ureters and collects in the urinary bladder, a muscular sac that stores it until voluntary excretion occurs via the urethra. This multi-stage system ensures that nitrogenous waste, particularly urea, is constantly removed from circulation, preventing toxicity and contributing to the body’s internal stability.
What are the key functions of the kidneys beyond urine production?
Although urine formation is the most visible function of the kidneys, these organs have several other critical roles in maintaining health. One of their core responsibilities is fluid and electrolyte regulation. Kidneys continuously monitor the concentration of water and various dissolved ions in the bloodstream. Depending on hydration status, they reabsorb water to conserve fluids or allow more to be excreted to maintain osmotic balance. This process keeps blood volume and cellular function stable.
The kidneys also regulate the body’s acid-base balance by secreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate. This chemical buffering is essential for preserving the blood’s pH within the narrow range necessary for enzyme activity and metabolic reactions. In addition to chemical regulation, the kidneys play a major role in controlling blood pressure. They release renin, an enzyme that triggers a hormonal cascade — the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system — which adjusts vascular tone and sodium retention based on the body’s needs.
Furthermore, the kidneys are endocrine organs. They secrete erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow in response to low blood oxygen. They also activate vitamin D into its hormonally active form, calcitriol, which enhances calcium absorption from the intestines. Collectively, these functions underscore the kidneys’ influence far beyond the confines of the urinary tract.
What is the role of electrolytes in kidney function?
Electrolytes are charged particles dissolved in body fluids that facilitate essential physiological processes. Sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride are the most critical among them. Their movement across membranes generates electrical impulses necessary for nerve transmission and muscle contraction. These ions also regulate water distribution across tissues, influence blood pressure, and stabilize cellular pH.
The kidneys control electrolyte levels through selective filtration and reabsorption. For example, when potassium levels rise, the kidneys excrete more potassium in the urine. Conversely, if sodium levels drop, hormonal signals promote sodium retention. This balance is constantly fine-tuned to adapt to dietary intake, fluid loss, and metabolic demand. Any disruption in this system, such as through kidney disease or dehydration, can lead to severe complications including muscle cramps, cardiac arrhythmias, and seizures. Thus, electrolyte regulation is not an ancillary function but a core responsibility of the renal system.
How do kidneys produce hormones and regulate distant organs?
The endocrine capabilities of the kidneys extend their physiological influence well beyond waste removal. One of the most notable hormones produced is erythropoietin. In states of hypoxia, or low oxygen availability, the kidneys sense the deficiency and release erythropoietin into the bloodstream. This hormone travels to the bone marrow, where it stimulates the production of red blood cells. More red blood cells enhance the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity, correcting the original imbalance.
Renin, another important molecule secreted by specialized cells in the kidneys, initiates a cascade that helps retain sodium and constrict blood vessels, increasing blood pressure. This system is especially vital during hemorrhage or dehydration when fluid conservation becomes urgent.
The kidneys also activate vitamin D into calcitriol. This hormonally active form of vitamin D allows the intestines to absorb dietary calcium efficiently. Without this step, calcium levels in the blood would fall, leading to bone resorption and metabolic disturbances. Moreover, the kidneys metabolize and inactivate circulating hormones like insulin and parathyroid hormone, showcasing their role in endocrine clearance and hormonal equilibrium. In all, the kidneys act as both producers and processors of hormones vital for systemic function.
What happens when kidney function is impaired?
Renal impairment disrupts every function outlined above and often triggers cascading systemic failures. One of the first signs of kidney dysfunction is a rise in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, indicating poor filtration of waste. As uremic toxins accumulate, patients may experience nausea, fatigue, cognitive changes, and inflammation.
Fluid imbalance often follows, resulting in swelling in the legs, hands, or lungs. If the kidneys cannot excrete potassium properly, dangerous levels may develop, potentially causing life-threatening arrhythmias. Blood pressure usually rises due to poor sodium clearance and dysregulation of renin signaling. In chronic cases, reduced erythropoietin output leads to anemia, while low calcitriol levels cause poor calcium absorption and secondary bone disease.
Patients with end-stage kidney failure require dialysis to manually filter their blood or a kidney transplant to restore systemic function. Given the multitude of systems affected, kidney health is now viewed as a major determinant of cardiovascular, hematologic, and skeletal wellness.
How is urine output regulated by the brain and hormones?
The volume and concentration of urine are not constant. Instead, they respond to the body’s hydration status through hormonal signals originating in the brain. When water levels in the body decrease — due to exercise, heat, or insufficient intake — the hypothalamus detects the rising concentration of solutes in the blood. It then prompts the posterior pituitary to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
ADH travels through the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it signals the collecting ducts to reabsorb more water and reduce urine output. This leads to more concentrated urine and helps conserve body fluids. When hydration improves, ADH levels drop, allowing the kidneys to release excess water as diluted urine. This system keeps blood osmolarity within optimal range and ensures stable blood pressure and cell function, illustrating the tight brain-kidney hormonal coordination.
How does the urinary system interact with modern medicine?
In contemporary healthcare, the urinary system plays a central role in diagnostics, pharmacology, and chronic disease management. Laboratory tests such as serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and blood urea nitrogen are standard tools to assess kidney function. Urinalysis — examining the physical and chemical properties of urine — reveals signs of infection, kidney damage, protein leakage, and metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Renal clearance also determines how drugs are metabolized and excreted. Medications such as antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, and blood pressure pills often require dose adjustments based on a patient’s kidney function to avoid toxicity. Furthermore, chronic kidney disease patients are frequently treated with recombinant erythropoietin, vitamin D analogues, and phosphate binders to compensate for impaired endocrine function. The urinary system, therefore, intersects with nearly every specialty in medicine, from internal medicine and endocrinology to cardiology and nephrology.
Why kidney function is essential to overall health
The kidneys are not merely urine-forming organs but are master regulators of homeostasis. They detoxify nitrogenous waste by transforming ammonia into urea, regulate the body’s fluid and electrolyte composition, maintain acid-base balance, and influence distant tissues through hormonal signaling. Their failure impacts multiple systems, from the cardiovascular and skeletal systems to red blood cell production and neural function.
In today’s era of precision medicine, where tailored treatment relies heavily on understanding organ function and systemic interactions, kidney health has never been more relevant. For medical professionals, physiology students, and anyone interested in how the body maintains balance, the urinary system offers a compelling lens into the complexity and intelligence of human biology.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






