What are the two major functions of the human ear?
The human ear performs two essential functions—enabling hearing and maintaining equilibrium. While it’s commonly associated with auditory perception, the ear is also a vital organ for detecting head movements and helping the body retain balance. Through a sequence of mechanical, hydraulic, and neural processes, the ear captures sound waves from the environment and relays them to the brain as electrical signals. Simultaneously, fluid-filled structures deep inside the ear monitor motion and orientation. These dual capabilities make the ear one of the most functionally diverse organs in the human body. Understanding how the brain interprets sound and how the body maintains balance begins with a deeper look into the structure of the ear itself.
How is the human ear divided into functional regions?
The human ear is anatomically divided into three interconnected regions, each with specialized parts and functions. The outer ear collects sound and funnels it inward. The middle ear amplifies mechanical vibrations. The inner ear processes both auditory and balance-related information. These three regions work in a synchronized sequence, ensuring that external vibrations and movements are accurately converted into meaningful sensory experiences. Their interdependence highlights how structural design supports multiple sensory roles within the same anatomical framework.
How does the outer ear collect and channel sound waves?
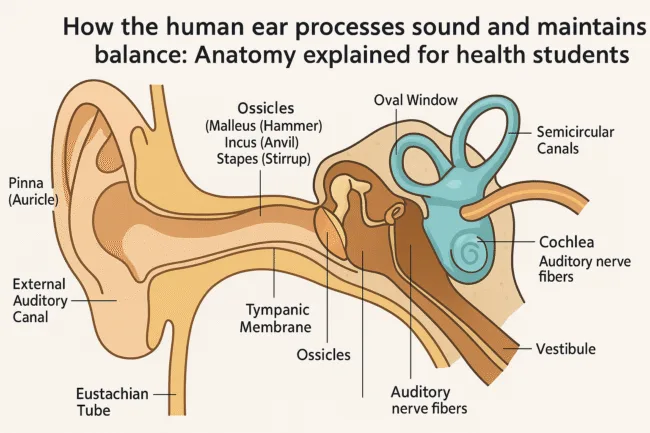
The outer ear includes both visible and internal passageways that form the first segment of the auditory system. The pinna, or auricle, is the external flap of the ear that gathers and directs sound into the auditory canal. Its curved shape helps localize sounds and determine their direction. Once sound enters the external auditory canal, it travels down a narrow tube lined with glands that secrete cerumen, more commonly known as earwax. This wax protects the ear by trapping dirt and microbes, while also preventing dryness and irritation. As sound continues its journey, it strikes the tympanic membrane, or eardrum, which is a thin, taut barrier that vibrates in response to the incoming pressure waves. This membrane marks the boundary between the outer and middle ear and initiates the process of mechanical amplification.
What happens in the middle ear after the eardrum vibrates?
The middle ear functions as a mechanical relay station, converting the vibrations of the tympanic membrane into amplified signals that can effectively stimulate the fluid-filled inner ear. As the eardrum vibrates, it moves a set of three small bones collectively known as the ossicles. These bones—the malleus, incus, and stapes—are linked in a chain-like fashion that increases the force of the vibrations while maintaining their frequency. The malleus connects directly to the tympanic membrane, and it passes motion to the incus, which in turn moves the stapes. The stapes is the smallest bone in the human body and interfaces directly with a membrane called the oval window, which acts as the portal to the inner ear. Another essential structure in the middle ear is the eustachian tube, a slender canal that connects the middle ear to the pharynx. This tube allows for pressure equalization between the inner and outer sides of the tympanic membrane, protecting it from rupture during sudden atmospheric changes and reducing the risk of infection.
What structures are found in the inner ear and what do they do?
The inner ear, often referred to as the labyrinth due to its intricate shape, is a complex chamber that houses both the cochlea and the vestibular system. These two components are responsible for hearing and balance, respectively. The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ that converts mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals through specialized fluids and receptor cells. In contrast, the vestibular system consists of structures that detect motion and orientation, helping the body maintain balance. Both systems are filled with fluids—perilymph and endolymph—that transmit movement through pressure changes, ensuring that both hearing and balance rely on similar mechanical and neural principles.
How does the cochlea transform vibrations into nerve impulses?
The cochlea plays a central role in auditory perception by translating mechanical energy into neural signals. Inside this coiled structure, vibrations from the stapes are transferred through the oval window into the cochlear fluids, specifically perilymph and endolymph. These fluid waves travel through the cochlear duct and stimulate the organ of Corti, a specialized sensory area embedded with thousands of hair cells. When these hair cells are bent by fluid movement, they trigger electrical impulses that are transmitted via the auditory nerve to the brain. This process allows the brain’s auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum, to interpret sound in terms of pitch, volume, and spatial origin. The cochlea’s ability to detect a wide range of frequencies with such precision is due to its tonotopic organization, where different regions of the cochlea are tuned to specific frequencies.
How does the vestibular system maintain balance and spatial orientation?
The vestibular system is responsible for sensing motion and position changes of the head and body. It includes the vestibule and three semicircular canals, each oriented at different angles to capture rotational movement along multiple planes. These canals are filled with endolymph, a viscous fluid that moves in response to head motion. Within the canals are hair cells embedded in gelatinous structures. When the head moves, the fluid lags due to inertia, causing the hair cells to bend and produce electrical signals. These signals travel through the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve to the cerebellum and brainstem, where they are processed and integrated with visual and proprioceptive input. This system allows for the fine-tuned control of posture, gaze stabilization, and balance during activities such as walking, running, or changing direction. Disruption in vestibular function can result in symptoms like dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance.
What is the full pathway of hearing from sound wave to brain interpretation?
The auditory pathway begins with the pinna collecting sound waves and directing them through the external auditory canal. These waves strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations are transmitted through the ossicles—malleus, incus, and stapes—to the oval window, which then sets the cochlear fluids in motion. Fluid movement inside the cochlea stimulates the hair cells in the organ of Corti, generating nerve impulses. These impulses are carried by the auditory nerve to the brainstem, where they pass through a series of relay centers before reaching the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. At this final stage, the brain interprets the signals as recognizable sounds, allowing humans to process language, music, and environmental cues with remarkable speed and accuracy.
What medical conditions can affect hearing and balance?
Several medical conditions can impair the auditory and vestibular functions of the ear. Otitis media, or middle ear infection, is common in children and may result in temporary hearing loss if not treated. Tinnitus, the perception of ringing or buzzing in the ears, often arises from damage to cochlear hair cells. Presbycusis refers to age-related hearing loss due to gradual degeneration of auditory receptors. Meniere’s disease is a chronic inner ear disorder that causes vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness in the ear. Barotrauma occurs when sudden pressure changes affect the eustachian tube’s ability to equalize, leading to discomfort and possible damage. Understanding the precise anatomy of the ear helps clinicians identify these conditions early and provide interventions such as antibiotics, hearing aids, cochlear implants, or vestibular rehabilitation.
Why is understanding ear physiology essential in healthcare today?
The study of the ear is critical for several branches of medicine including otolaryngology, audiology, neurology, and even physical therapy. As medical technology advances, understanding how the brain controls hearing and balance becomes increasingly important. Conditions affecting the auditory and vestibular systems often have overlapping symptoms, and precise anatomical knowledge can aid in accurate diagnosis. Moreover, early signs of hearing loss or balance issues often go unnoticed, especially in older adults. Public health initiatives and clinical screening programs rely on a foundational understanding of ear physiology to detect problems early and guide effective treatment strategies. This is especially relevant today with the growing use of hearing aids, balance therapies, and surgical interventions like cochlear implants.
The ear’s dual sensory power and its role in modern medicine
The human ear exemplifies how structure and function work together to support both hearing and balance. Its intricate design allows for the conversion of simple mechanical waves into complex neurological responses, enabling us to perceive the world and maintain orientation within it. The dual sensory roles of the cochlea and vestibular system reflect a finely tuned biological mechanism that underpins communication, mobility, and safety. In the context of modern medicine, this knowledge not only aids clinical practice but also supports the development of new technologies for restoring or enhancing sensory function. Whether you’re a student, health practitioner, or curious reader, understanding how the ear works offers a gateway into broader discussions about sensory integration, brain function, and the human experience.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








