Endocrine glands are silent regulators that influence nearly every system in your body. These ductless glands release chemical messengers called hormones directly into the bloodstream, allowing communication between organs that are often far apart. From managing blood sugar levels to guiding reproductive health and mood, endocrine glands are central to maintaining internal balance. Unlike exocrine glands—such as sweat glands or salivary glands—which release substances through ducts onto surfaces or into cavities, endocrine glands send their hormonal secretions straight into the circulatory system. These hormones then travel to specific target organs, binding to receptors and triggering changes that keep the body functioning smoothly. The endocrine system works hand in hand with the nervous system to coordinate complex physiological tasks. While the nervous system acts rapidly, often within milliseconds, the endocrine system provides sustained, longer-term regulation. This makes it especially crucial for ongoing functions like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and homeostasis.
What is a gland and how does it function?
In biological terms, a gland is a group of specialized cells that synthesizes and secretes substances needed by the body. Glands are classified into two broad types: endocrine and exocrine. The distinction lies in how and where their secretions are released. Exocrine glands discharge their secretions—such as mucus, enzymes, or sweat—through ducts either onto body surfaces or into hollow organs. Their effects are usually localized and short-lived. In contrast, endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream without using ducts. These hormones circulate widely, acting as chemical messengers that influence distant organs or tissues. Because they act systemically and often over extended durations, hormones help regulate the body’s overall stability and adaptability to changing internal and external environments.
How are endocrine and exocrine glands different?
While both types of glands play vital roles, their mechanisms and effects differ dramatically. Endocrine glands participate in long-distance communication inside the body, influencing everything from emotional states to cellular energy production. Hormones released by endocrine glands often have prolonged effects and act on multiple body systems. Exocrine glands, on the other hand, typically have immediate and localized effects. For example, sweat glands help control body temperature by releasing moisture onto the skin’s surface, while salivary glands aid digestion by secreting enzymes into the mouth. Their secretions exit through ducts and do not enter the bloodstream. One organ—the pancreas—functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces insulin and glucagon (hormones that regulate blood sugar) for endocrine function, while also releasing digestive enzymes into the small intestine via ducts, fulfilling an exocrine role. This dual capability highlights the interwoven nature of human physiology.
Where are endocrine glands located in the body?
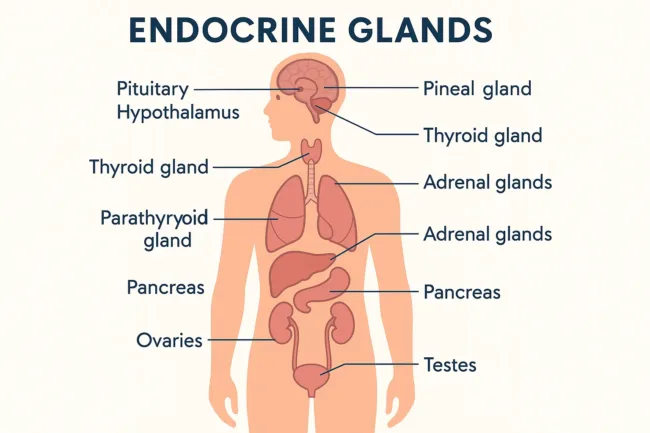
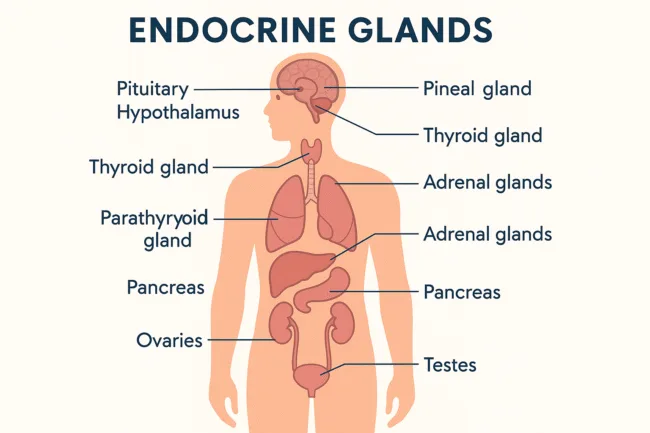
Endocrine glands are strategically distributed throughout the human body. Each gland has a unique location and function, collectively ensuring that various physiological systems work in harmony. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and is often referred to as the “master gland” because it controls several other endocrine glands through hormone signals. Just above it, the hypothalamus links the nervous and endocrine systems by regulating pituitary hormone release. The thyroid gland, found in the neck, governs metabolism and energy usage, while the smaller parathyroid glands located behind it regulate calcium balance. The adrenal glands sit above each kidney and manage stress responses through hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. The pancreas, located behind the stomach, plays a dual role in blood sugar regulation and digestion. Deep within the brain lies the pineal gland, which helps regulate sleep patterns via melatonin. In the reproductive system, the ovaries in females and testes in males control hormone production for sexual development and fertility. These glands are richly supplied with blood vessels to ensure their secretions reach target tissues quickly and efficiently.
What hormones do endocrine glands release and what do they do?
Each endocrine gland secretes one or more specific hormones, each of which has a defined set of roles. The pituitary gland secretes growth hormone, prolactin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone. These hormones control growth, lactation, and the activity of the thyroid gland. The thyroid produces thyroxine and triiodothyronine, which regulate metabolism, heart rate, and temperature. The adrenal glands secrete cortisol, which helps manage stress and metabolism, and aldosterone, which maintains blood pressure and fluid balance. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, which work together to regulate blood glucose levels. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone to govern menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and secondary female characteristics, while the testes produce testosterone, essential for male reproductive functions and muscle development. Hormones are incredibly potent chemical signals. Even in very small amounts, they can trigger significant biological responses by binding to specific receptors on their target cells. Once bound, these hormone-receptor interactions can activate or suppress gene expression, influence enzyme activity, or adjust the metabolic behavior of cells to adapt to current body demands.
How are hormone levels regulated in the body?
Hormone levels in the body are tightly regulated to maintain internal balance, a process known as homeostasis. This is primarily achieved through feedback loops—particularly negative feedback mechanisms. These loops allow the endocrine system to self-regulate by adjusting hormone output based on circulating levels. For instance, if thyroid hormone levels rise above optimal, the hypothalamus reduces its release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), and the pituitary decreases secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), effectively slowing down thyroid hormone production. When levels drop, the opposite occurs. This feedback control maintains hormone levels within precise ranges and prevents overproduction or deficiency. The liver also plays a critical role by breaking down hormones that are no longer needed, and the kidneys help eliminate them through urine. These systems work in concert to ensure that hormonal fluctuations are temporary and kept within biologically acceptable limits.
Why is the endocrine system essential for health and survival?
The endocrine system supports the foundational processes that keep you alive and functioning. It helps the body grow from infancy to adulthood, enables it to adapt to stress, maintains stable energy levels, supports reproductive health, and allows for healing and recovery. The hormones released by endocrine glands ensure that your cells, tissues, and organs operate in coordination with one another, even when conditions outside the body change rapidly. Disruptions in hormone balance can result in a variety of diseases. Hypothyroidism may lead to fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Overactive adrenal glands can result in anxiety and high blood pressure. Diabetes results from problems in insulin production or response. Even subtle imbalances can impact mood, sleep, fertility, and immune system function. Recognizing the signs of endocrine disorders is key to early diagnosis and treatment. Therapies can range from hormone replacement and medications to lifestyle modifications, depending on the nature of the imbalance. Regular checkups and diagnostic testing help identify abnormalities before they cause long-term complications.
How do modern therapies target endocrine gland dysfunction?
Modern medicine offers a wide array of treatments for endocrine gland dysfunction. Diagnostics have improved with hormone assays, medical imaging, and genetic testing, allowing physicians to pinpoint the exact source of imbalance. Hormone replacement therapy is one of the most widely used interventions, especially in cases of hypothyroidism, menopause, and growth hormone deficiency. In diseases like diabetes, insulin therapy and blood sugar monitoring are essential. Some conditions require surgical removal of tumors or hyperactive glands, while others benefit from medications that modulate hormone receptors or inhibit hormone synthesis. Advances in biotechnology have led to the creation of synthetic and long-acting hormones, which are more effective and convenient for patients. Digital health tools, including wearables and smartphone-linked glucose monitors, now allow for real-time tracking of hormone-related markers such as insulin or cortisol levels. These innovations enable more personalized treatment and early warning systems for dangerous fluctuations. As research progresses, newer therapies like gene editing, stem cell applications, and AI-guided hormonal modeling are likely to revolutionize how we manage endocrine disorders in the future.
What is the relevance of endocrine glands in modern physiology?
Endocrine glands are not just background players in human biology—they are frontline regulators that ensure your body’s internal operations continue without interruption. Their influence is so extensive that nearly every chronic disease, mental health condition, and metabolic disorder has some hormonal component. In today’s modern lifestyle—marked by irregular sleep, poor diet, chronic stress, and sedentary behavior—the risk of endocrine imbalances has increased. Hormonal health has become a priority in both preventive and therapeutic medicine. Whether addressing infertility, managing weight, enhancing cognitive performance, or improving sleep, a clear understanding of endocrine function allows both healthcare providers and individuals to make informed decisions. Public awareness around thyroid disorders, PCOS, adrenal fatigue, and testosterone decline is growing, prompting earlier intervention and better outcomes. As the world shifts toward integrative medicine and personalized care, understanding the endocrine system will remain foundational to optimizing health and preventing disease.
Why should you understand your endocrine glands?
Your endocrine glands are the body’s chemical control centers, orchestrating the rhythms of metabolism, growth, mood, immunity, and reproduction. Even though they are invisible to the eye and operate quietly in the background, their effects are constant and vital. Understanding how they work, where they are located, and what happens when they malfunction empowers you to take control of your health. Whether you are studying medicine, managing a chronic condition, or simply optimizing your wellbeing, having a basic grasp of the endocrine system will help you detect early warning signs, make better lifestyle choices, and communicate more effectively with your healthcare provider. Hormonal health is not just a medical concept—it is a day-to-day reality that affects how you think, feel, and function.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.