How do OpenAI o3 and o4-mini redefine the capabilities of general-purpose AI models?
OpenAI has expanded the capabilities of general-purpose artificial intelligence with the introduction of o3 and o4-mini, two new models in its o-series architecture. These models represent a significant advance in AI reasoning, integrating full tool usage into ChatGPT for the first time and allowing for greater autonomy in problem-solving. They are built to think more deeply before responding and can decide when and how to use available tools—including web browsing, Python-based data analysis, and image manipulation—to deliver more context-aware, multimodal answers.
The o3 model stands as OpenAI’s most capable reasoning model to date, while o4-mini has been optimised for speed, throughput, and affordability. Despite being smaller, o4-mini achieves exceptional benchmark performance, making it suitable for high-volume applications such as customer interaction, content review, and educational assistance. These two models have been rolled out to ChatGPT Plus, Pro, and Team users, and are now accessible via API, offering scalable deployment for businesses, developers, and researchers.
This launch marks a strategic convergence of agentic planning, real-time tool orchestration, and cross-modal thinking within a single AI platform, moving OpenAI’s ecosystem toward more autonomous and adaptable AI agents.
What differentiates o3 and o4-mini in terms of reasoning power and real-world performance?
OpenAI o3 is built for advanced, multi-step problem-solving. It sets a new standard for AI performance on a variety of complex benchmarks, particularly in science, programming, visual reasoning, and mathematics. Its agentic reasoning capabilities allow it to evaluate when to trigger tool use and how to sequence multiple actions to achieve an outcome. This is a significant step toward task-oriented autonomy in AI.
The o4-mini model, while smaller and more cost-efficient, delivers top-tier performance within its class. On benchmark tests such as the American Invitational Mathematics Examination (AIME) for 2024 and 2025, o4-mini surpassed all previous small models, achieving accuracy rates above 92%. It also performed exceptionally well on software engineering and research-oriented tasks, such as SWE-Bench and GPQA, where complex domain knowledge and structured reasoning are essential.
When comparing performance across visual understanding tasks, both o3 and o4-mini exceeded expectations. They demonstrated improved accuracy on benchmarks like MMMU (college-level multimodal problem-solving) and CharXiv-Reasoning (scientific visual analysis). These outcomes highlight the models’ capacity to synthesise visual and textual data within structured reasoning chains, marking a distinct departure from earlier generations of language models.
How does agentic tool use enhance task execution in OpenAI’s latest models?
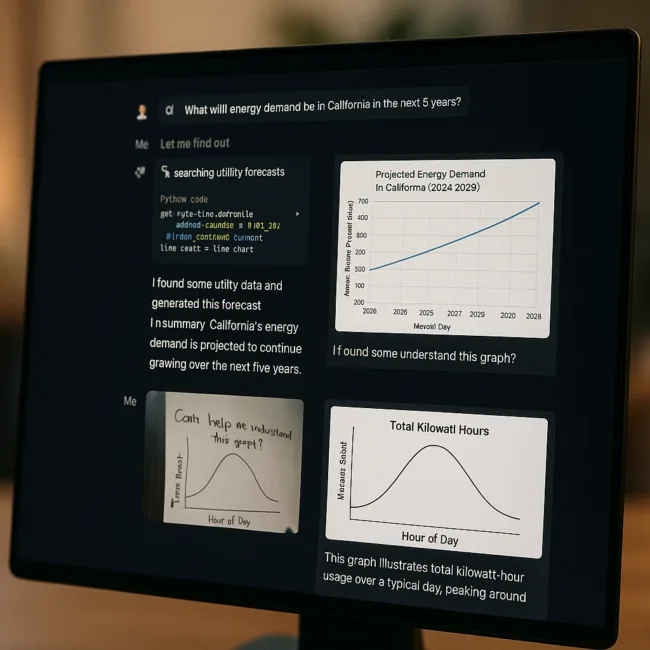
One of the core innovations in o3 and o4-mini is their ability to autonomously use tools based on the requirements of a task. Rather than waiting for users to manually initiate tool use, these models reason about when a tool is necessary, choose the appropriate method, and apply it within a coherent response framework. This behaviour mirrors that of a human assistant capable of using a calculator, search engine, or charting tool based on contextual needs.
For instance, when asked about future energy demand in California, the o3 model can search for utility data, execute Python code to generate a forecast, create a chart for visualisation, and provide an explanatory summary—linking tools in a logical sequence within seconds. This approach allows for faster, more accurate, and more verifiable outputs that extend well beyond static text generation.
These models also support the integration of custom developer tools via function calling, opening the door to bespoke workflows in sectors such as legal analysis, financial modelling, healthcare diagnostics, and academic research. Developers can now build AI agents that reason independently, apply tools strategically, and deliver structured outputs across multiple formats.
What are the key advancements in multimodal reasoning capabilities?
OpenAI’s o3 and o4-mini models incorporate advanced multimodal reasoning, enabling them to interpret and interact with visual data as part of their decision-making process. This goes beyond basic image recognition. These models can ingest whiteboard photographs, textbook diagrams, or hand-drawn sketches—even if low-resolution or rotated—and incorporate them into broader logical reasoning workflows.
Multimodal integration allows the models to perform tasks that involve simultaneous visual and textual understanding. For example, they can extract mathematical relationships from graphs, annotate images with context-aware labels, or reason about spatial layouts in engineering diagrams. By merging vision and language processing into a single coherent stream, these models unlock applications in technical support, scientific research, and visual data analytics.
In practical terms, this means a user could upload a blurry classroom slide and ask a complex question about the graph’s content. The model would process the image, link it to known statistical or scientific principles, and generate a text explanation or even a corrected version of the graph. This represents a substantial improvement over models that treat image understanding as a standalone capability.
How are developers and enterprises integrating these models into workflows?
OpenAI has enhanced developer access through the launch of Codex CLI, a lightweight command-line tool that allows direct integration of o3 and o4-mini models into local development environments. Developers can pass screenshots, snippets of code, or sketches to the model alongside traditional inputs. This enables highly customised multimodal problem-solving from the terminal.
Codex CLI is available as an open-source project on GitHub and is part of a broader push by OpenAI to support community experimentation. A $1 million grant initiative has also been launched to support novel use cases of Codex CLI and the o-series models. Grants are offered in $25,000 API credit blocks for approved project proposals.
For enterprise users, the Chat Completions API and Responses API now support deeper reasoning integrations, with planned support for built-in tools such as file search and code execution. These APIs allow for reasoning-aware responses, retention of tool context, and precise interaction sequencing, ideal for building intelligent assistants or automation agents in business environments.
OpenAI has also announced that access to o3 and o4-mini will be rolled out to ChatGPT Enterprise and Edu users within a week of the initial release, expanding availability for institutional applications.
What does this mean for the competitive AI landscape?
OpenAI’s latest models position the company at the forefront of agentic and multimodal AI development. While competitors like Anthropic (Claude), Google DeepMind (Gemini), and Mistral have demonstrated progress in conversational fluency, retrieval capabilities, and open-source model performance, OpenAI’s o-series now defines the frontier in integrated reasoning, tool use, and visual problem solving.
Unlike the GPT-series, which was tuned primarily for conversational natural language processing, the o-series has been trained to make decisions about how to solve a problem, not just what to say. This strategic shift gives OpenAI a significant edge in use cases that demand higher cognitive function, autonomous workflow execution, and real-time tool orchestration.
This evolution also blurs the line between chatbot and task agent. The o3 and o4-mini models are not only conversational but also executable—they can reason, retrieve, compute, visualise, and adjust—all within the same interaction session. This multidimensional ability is expected to define the next wave of AI platform development.
With the upcoming release of o3-pro, which will include enhanced capabilities and extended memory, OpenAI is further positioning itself to compete across both consumer and enterprise segments by delivering scalable reasoning as a service.
The launch of OpenAI’s o3 and o4-mini models marks a new phase in the development of general-purpose AI—where multimodal understanding, tool-based action, and autonomous planning converge into a single platform. Whether used for research, development, business automation, or educational augmentation, these models set a new benchmark for what AI can accomplish in reasoning, responsiveness, and real-world problem-solving.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






