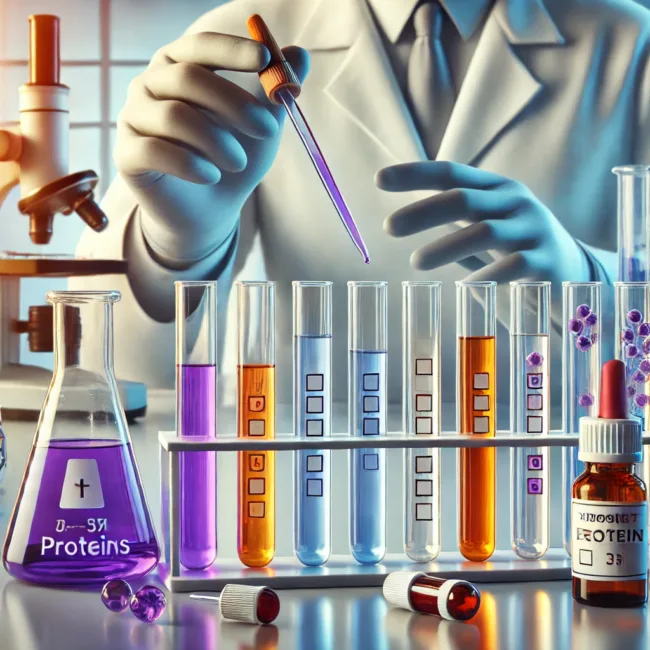
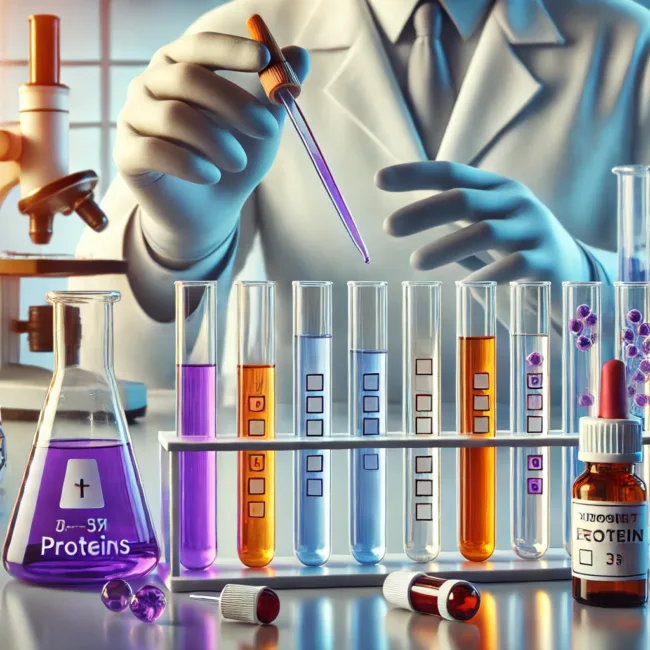
Proteins are essential biomolecules that play a fundamental role in biological systems. Whether in medical research, food science, or pharmaceuticals, identifying proteins accurately is crucial. Various chemical tests are designed to detect proteins by reacting with specific functional groups within their structure. The Biuret test for proteins, the Xanthoproteic test reaction, and the Ninhydrin amino acid test are among the most widely used methods in laboratory analysis. Understanding how these tests work provides valuable insights into protein composition and quality.
Why is protein detection important?
Protein analysis is critical across multiple industries. In food science, verifying protein content ensures accurate labeling and compliance with nutritional standards. Medical and pharmaceutical fields rely on protein detection to study enzymes, antibodies, and other biological molecules. Additionally, forensic scientists use protein tests in investigations, while researchers in biotechnology assess protein purity in drug development.
The Biuret test: A reliable method for detecting proteins
One of the most widely used protein detection methods is the Biuret test for proteins, which identifies peptide bonds linking amino acids. When Biuret reagent, containing copper sulfate, is added to a solution, it reacts with these bonds, producing a violet color if proteins are present. The intensity of the violet hue indicates the concentration of proteins in the sample. This test is commonly used in biochemical research and clinical laboratories for analyzing protein content in blood, food, and pharmaceutical products.

Heat coagulation test: Understanding protein denaturation
Proteins are sensitive to heat, and this property is exploited in the heat coagulation test. When a protein solution is heated in a boiling water bath, the proteins denature and precipitate out. This reaction occurs because heat disrupts the hydrogen bonds maintaining protein structure, leading to coagulation. A common example is egg whites solidifying when cooked, a visible demonstration of protein denaturation. This test is particularly useful in food science and medical diagnostics, where abnormal protein coagulation may indicate certain diseases.
Trichloroacetic acid test: Precipitating proteins from solutions
Another effective method for protein detection is the trichloroacetic acid precipitation test. Adding trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to a protein solution causes immediate precipitation. This reaction occurs because TCA disrupts protein solubility, leading to aggregation and the formation of an insoluble mass. This test is widely used in laboratories to isolate proteins from complex mixtures, helping researchers analyze protein purity and composition.
Hydrolysis and the Ninhydrin test for amino acids
Proteins can be broken down into their building blocks—amino acids—through acid hydrolysis using hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. Once hydrolyzed, the solution is tested with Ninhydrin reagent, which reacts specifically with free amino acids. A positive reaction produces a deep purple or blue color, confirming the presence of amino acids derived from protein breakdown. This test is essential in protein metabolism studies, where researchers analyze how proteins are digested and utilized by the body.
Xanthoproteic test: Identifying aromatic amino acids in proteins
The Xanthoproteic test reaction is used to detect aromatic amino acids such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine within proteins. When concentrated nitric acid is added to a protein solution and heated, a yellow precipitate forms. After cooling, the addition of sodium hydroxide changes the color to orange, confirming the presence of aromatic amino acids. This test is particularly useful in studying protein composition in biological and food samples.
Applications of protein detection in various industries
Protein detection methods have broad applications across different sectors. In food science, these tests help verify protein content in dairy, meat, and plant-based products, ensuring consumers receive accurate nutritional information. In clinical diagnostics, protein analysis is used to detect diseases such as kidney disorders, where abnormal protein levels in urine signal potential health concerns. The pharmaceutical industry relies on these tests to study protein-based drugs, including monoclonal antibodies and enzyme-based treatments.
How protein tests improve scientific research
Protein detection techniques are essential tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. Researchers use these methods to study protein structure, function, and interactions, providing insights into genetic disorders, metabolic pathways, and disease mechanisms. The Biuret test for proteins, the Xanthoproteic test reaction, and the Ninhydrin amino acid test contribute to groundbreaking discoveries in medical and environmental sciences, helping scientists develop new treatments and sustainable solutions.
Accurate protein detection is crucial for scientific research, healthcare, and industry applications. The Biuret test for proteins, the Xanthoproteic test reaction, and the Ninhydrin amino acid test provide reliable methods for identifying and analyzing proteins in various samples. Understanding these chemical tests enhances our ability to study biological systems, improve food quality, and develop innovative medical treatments. As science continues to advance, protein analysis will remain an essential tool in research and industry, driving new discoveries and technological advancements.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.