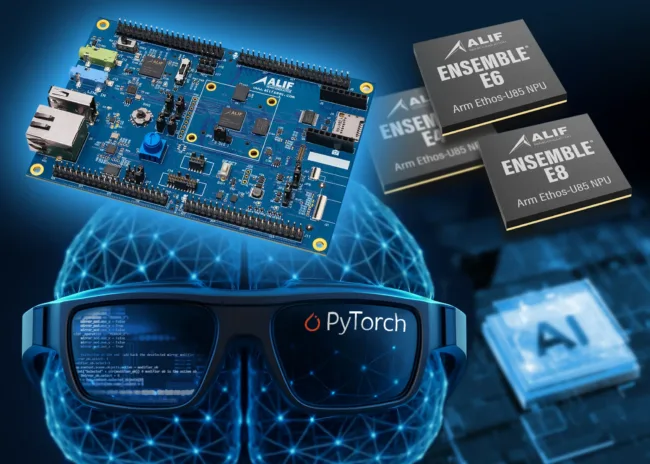
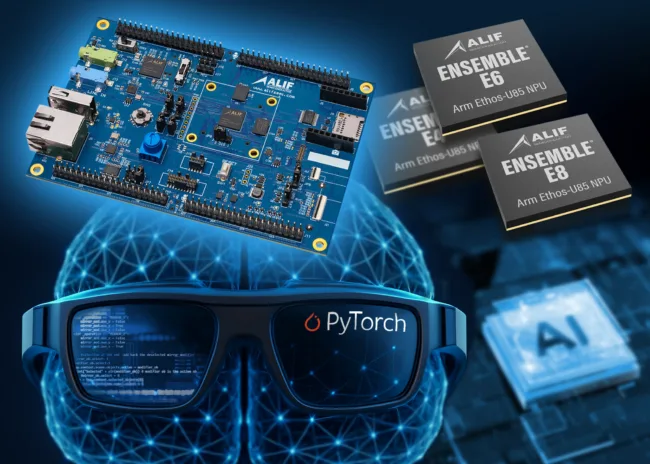
Alif Semiconductor has expanded the capabilities of its Ensemble microcontroller and fusion processor series by announcing official support for the ExecuTorch Runtime, a PyTorch-compatible quantization extension that enables efficient deployment of transformer-based generative AI models on edge and endpoint hardware. This move allows developers to bring advanced AI inference directly to battery-powered devices using the Ensemble E4, E6, and E8 microcontrollers, setting a new standard in low-power embedded intelligence.
The announcement was timed to coincide with demonstrations at the PyTorch Conference held in San Francisco in late October 2025, where Alif Semiconductor and Arm jointly showcased use cases running on the Ensemble E8. These included a compact language model that generated children’s stories in response to visual prompts and an on-device real-time speech-to-text system integrated into a wearable format such as smart glasses. Both examples underscored the platform’s ability to run high-performance AI workloads locally, without relying on cloud compute.
Alif Semiconductor, headquartered in California, has built a reputation as a supplier of secure, connected, power-efficient microcontrollers and fusion processors designed for artificial intelligence and machine learning workloads. Since its founding in 2019, the company has targeted developers of IoT and embedded systems looking to integrate more intelligence at the edge. With this latest announcement, Alif Semiconductor has positioned itself as a front-runner in enabling generative AI on microcontrollers, a domain typically constrained by strict power, memory, and compute limitations.

How does ExecuTorch Runtime support transform development for embedded AI systems?
ExecuTorch, a runtime extension of the PyTorch framework, enables developers to quantize and optimize machine learning models so they can run on resource-limited hardware. Traditionally, deploying models trained in PyTorch to embedded systems required complex conversions or use of separate toolchains. By supporting ExecuTorch directly on the Ensemble E4, E6, and E8 microcontrollers, Alif Semiconductor eliminates a major barrier for developers by streamlining the deployment path from training to edge inference.
The integration allows AI developers to build models using the familiar PyTorch workflow and seamlessly target Alif Semiconductor hardware for deployment. The Ensemble series, which includes the Arm Ethos-U85 neural processing unit, provides the required acceleration to support transformer-based networks in real time. This combination of PyTorch compatibility, hardware acceleration, and power efficiency opens the door to entirely new classes of intelligent applications that can run autonomously at the network edge.
Alif Semiconductor emphasized that these capabilities are not limited to niche or experimental projects. Instead, they are aimed squarely at scalable use cases in sectors including smart homes, robotics, healthcare and diagnostics, education technology, transportation systems, toys, and smart city infrastructure. The company highlighted that its devices are capable of high-accuracy, low-latency inference even in constrained power environments.
Why is this a strategic inflection point for microcontroller adoption in generative AI?
The ability to run generative AI models locally on microcontrollers changes the equation for product designers and original equipment manufacturers. Until now, most generative AI applications were confined to server-side infrastructure or high-end edge processors, given the memory and compute demands of large language and transformer models. Alif Semiconductor’s support for ExecuTorch Runtime demonstrates that it is now technically feasible to achieve meaningful generative AI inference on sub-watt devices.
This shift reduces the dependency on cloud infrastructure for AI workloads, enabling real-time decision-making, lowering latency, and enhancing data privacy. In many use cases, especially in healthcare and industrial settings, on-device AI can reduce operational complexity while keeping sensitive data local. For developers, the seamless PyTorch integration means they can continue using widely adopted open-source tools without needing to learn proprietary frameworks or workarounds.
Alif Semiconductor’s architecture also allows for simultaneous AI and control workloads, thanks to its fusion processor design. This design integrates multiple cores along with the neural processing unit, enabling the Ensemble MCUs to run inference alongside traditional microcontroller functions such as sensor control and connectivity management. This makes the Ensemble family particularly attractive for OEMs looking to consolidate functionality and reduce bill of materials costs.
What are the key use cases demonstrated, and how do they reflect broader industry trends?
At the 2025 PyTorch Conference, Alif Semiconductor and Arm demonstrated how transformer-based models could be used to generate content and interpret speech in real time on embedded devices. The first use case featured a compact language model capable of generating context-appropriate children’s stories from visual prompts, running entirely on the Ensemble E8. The second demonstration involved real-time transcription of speech to text on wearable smart glasses, showcasing how live captioning and accessibility features can be embedded directly into consumer hardware.
These examples point to a growing demand for smarter, more context-aware edge devices that can understand and respond to human input naturally. As generative AI becomes more integrated into everyday products, the ability to execute models on-device becomes a critical enabler. Alif Semiconductor’s solution also aligns with rising interest from sectors such as education, where toys and learning devices increasingly require speech and language processing, and smart cities, where low-latency, private AI is essential for public systems.
The company confirmed that its DK-E8 development board, which supports the entire Ensemble MCU family, is already available to developers. This allows for immediate prototyping and testing of PyTorch-trained models using the ExecuTorch Runtime.
How is Alif Semiconductor’s ExecuTorch Runtime launch being received by developers, analysts, and the wider edge AI ecosystem in 2025?
While Alif Semiconductor remains privately held and does not report financials publicly, institutional sentiment around edge AI has been increasingly optimistic. Analysts following the embedded systems and semiconductor sector have noted that enabling PyTorch-based model deployment on low-power hardware fills a critical gap in the AI development ecosystem. The ability to unify training and deployment under a single toolchain is expected to lower development costs, shorten time-to-market, and expand the addressable market for intelligent devices.
From a developer perspective, the new support allows more fluid experimentation and scaling. Instead of rewriting models or relying on third-party optimizers, engineers can now quantize and run their models on hardware that is purpose-built for efficiency. Alif Semiconductor is effectively extending the PyTorch developer ecosystem into embedded product categories where AI had previously been difficult or impossible to implement.
The broader edge AI market is expected to grow significantly in 2026 and beyond, as demand increases for autonomous systems, privacy-preserving inference, and reduced reliance on cloud infrastructure. Alif Semiconductor is well-positioned to benefit from this trend, especially if it can scale its hardware footprint through OEM partnerships or module integrations.
What should OEMs and product designers monitor going forward?
Original equipment manufacturers and developers looking to build smart devices should closely watch Alif Semiconductor’s Ensemble ecosystem, particularly as the integration of ExecuTorch matures. Factors such as development tool support, model conversion workflows, power-performance benchmarks, and memory optimization will determine how quickly these capabilities can be brought into production environments.
The release also signals an opportunity for new kinds of products—compact, responsive, and fully autonomous devices capable of local inference without dependence on 5G, Wi-Fi, or server backends. This could impact everything from children’s toys and personal health monitors to industrial robotics and voice-enabled appliances.
Alif Semiconductor’s ability to partner across the AI stack—from silicon to software—places it in a unique position to catalyze new applications of generative AI that operate quietly and intelligently at the edge. The key to unlocking value will be ease of adoption, competitive pricing, and continued support for industry-standard frameworks like PyTorch.
Is Alif Semiconductor setting the new baseline for AI-capable MCUs?
The announcement of ExecuTorch Runtime support across Alif Semiconductor’s Ensemble MCU series is a significant moment in the evolution of embedded AI. It brings together developer-centric software tools and advanced hardware architecture in a way that empowers edge devices to act with intelligence and autonomy. In a market where the line between endpoint and server is increasingly blurred, Alif Semiconductor’s innovations are helping to redefine what is possible on the smallest devices.
By making transformer-based inference viable on microcontrollers, Alif Semiconductor is expanding the range of applications that can benefit from generative AI. It also sends a strong signal to competitors in the embedded space that AI capability must now be part of the core offering, not just an add-on. The edge is getting smarter—and Alif Semiconductor is making sure it happens faster than anyone expected.
Key takeaways from Alif Semiconductor’s ExecuTorch Runtime integration for edge AI deployment
- Alif Semiconductor has added native support for the ExecuTorch Runtime to its Ensemble E4, E6, and E8 series of microcontrollers and fusion processors, enabling deployment of transformer-based generative AI models on battery-powered edge devices.
- The update bridges the PyTorch training environment with embedded hardware deployment, allowing developers to train models in PyTorch and deploy them efficiently to Alif Semiconductor’s hardware using ExecuTorch.
- Live demos at the 2025 PyTorch Conference showcased real-time speech-to-text and generative storytelling AI models running entirely on the Ensemble E8 processor without cloud connectivity.
- The Ensemble MCUs include the Arm Ethos-U85 NPU, delivering low-latency and high-accuracy inference performance for generative AI applications in areas such as wearables, robotics, diagnostics, smart homes, and smart city endpoints.
- Alif Semiconductor’s move reflects a strategic expansion of on-device intelligence, lowering latency, enhancing data privacy, and reducing reliance on cloud-based infrastructure.
- Developers can now leverage a seamless development pipeline using PyTorch and ExecuTorch, significantly reducing deployment friction in embedded AI projects.
- Institutional sentiment is optimistic, with analysts noting that the integration positions Alif Semiconductor well in the expanding edge AI market and developer ecosystem.
- The DK-E8 development board supporting the Ensemble MCU lineup is commercially available, enabling immediate prototyping and adoption by OEMs.
- The launch positions Alif Semiconductor as a front-runner in edge-deployed generative AI, making transformer inference viable on ultra-low-power microcontrollers for the first time.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.