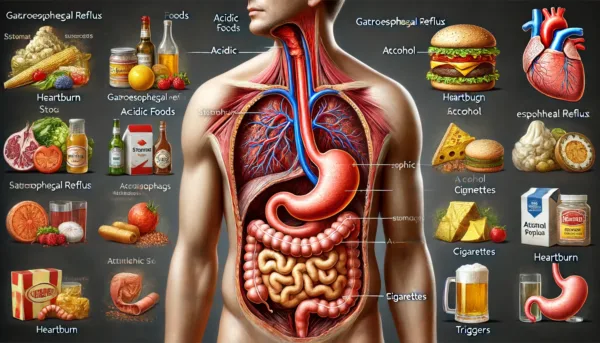
Heartburn, commonly associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a prevalent condition that affects many people worldwide. It typically manifests as a burning sensation starting behind the breastbone and extending up to the neck and throat, often worsening after eating or when lying down.
What Causes Heartburn?
Heartburn occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, the tube connecting the mouth and stomach. This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential damage. Several factors contribute to the likelihood of experiencing heartburn:
– Dietary Triggers: Consuming certain foods like tomatoes, citrus fruits, spicy foods, chocolates, and fatty foods can increase acid production.
– Lifestyle Factors: Alcohol intake, smoking, and stress can exacerbate heartburn symptoms.
– Physical Conditions: Pregnancy, obesity, and certain medical conditions like diabetes and asthma also heighten the risk.
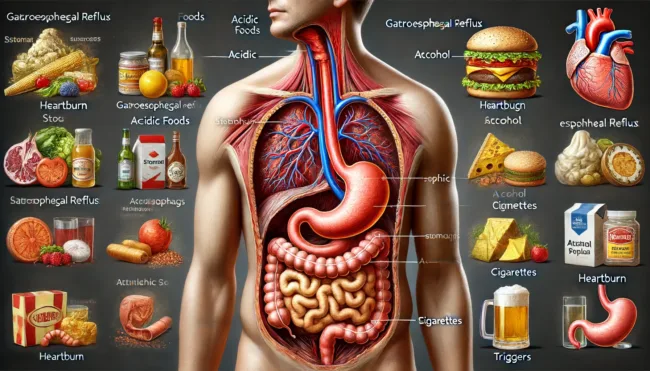
Symptoms of Heartburn
The primary symptom of heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest, often accompanied by:
– Sour Taste and Swallowing Difficulties: A sour or bitter taste in the mouth and difficulties swallowing are common.
– Regurgitation: Feeling of food re-entering the mouth or throat.
– Respiratory Problems: In some cases, heartburn can mimic asthma symptoms, such as wheezing and coughing, due to acid reflux affecting the lungs.
Effective Treatment and Management
While occasional heartburn can be managed with over-the-counter antacids, chronic heartburn may require more structured treatment:
– Lifestyle Changes: Adjusting diet, reducing alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and avoiding eating late at night can significantly reduce symptoms.
– Medication: For persistent heartburn, medications such as proton pump inhibitors or H2 receptor blockers may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid and heal the esophagus.
– Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter.
Preventive Measures
Preventing heartburn involves a combination of dietary management, lifestyle modifications, and, if necessary, medical treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down immediately after eating are practical steps that can minimize the incidence of heartburn.
Understanding the triggers and mechanisms of heartburn is crucial for effective management. With appropriate lifestyle changes and treatment, most people can achieve substantial relief from heartburn and prevent potential complications associated with GERD.
Discover more from Business-News-Today.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.